section-1414e32

section-018cc4c
Conditions affecting the upper and lower back can have a serious impact on mobility and overall quality of life. Patients experiencing symptoms of scoliosis, sciatica, SIJ dysfunction, spinal stenosis, low back osteoarthritis, and lumbar discopathy should seek medical attention as soon as possible to lower their risk of long-term health problems.
Back pain
Back pain may range from a muscle ache to a shooting, burning, or stabbing sensation. The pain may be localized, or radiate down the leg, and worsen with certain motions, such as twisting, bending, lifting, standing, or walking. Patients should see a doctor if their back pain:
- Persists for more than two weeks
- Is severe and doesn’t lessen after rest
- Radiates down one or both legs
- Leads to weakness, numbness, or tingling in one or both legs
- Leads to unexplained weight loss
Back pain may indicate a range of serious conditions that shouldn’t be ignored. During an appointment with an orthopedic physician, he or she will evaluate the patient’s symptoms and order the necessary diagnostic exams before creating a personalized treatment plan.
section-24f3387
section-c8617d2
Scoliosis
A sideways curvature of the spine, typically diagnosed in adolescents, is a spinal condition called scoliosis. Most cases are mild, but the curvature may worsen and reduce the amount of space within the chest, impacting breathing.
Scoliosis may be caused by certain neuromuscular disorders, birth defects, spinal injuries or infections, spinal cord abnormalities, and previous pediatric surgery to the chest wall. Depending on the severity of the condition, patients may need to wear a brace or undergo surgery.
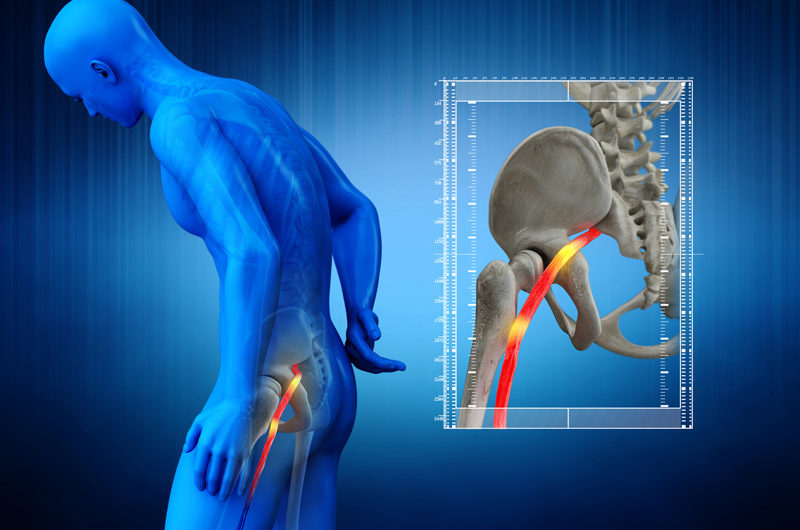
Sciatica
Sciatica is characterized by pain that radiates along the path of the sciatic nerve, which extends from the lower back through the hips and buttocks down each leg. The condition may be caused by a herniated disc, bone spur on the spine, or spinal stenosis that compresses part of the nerve.
Physicians will need to see imaging scans before they can diagnose patients with sciatica. Treatment options include medication, physical therapy, steroid injections, and surgery.
section-a2456fe
section-c301c03
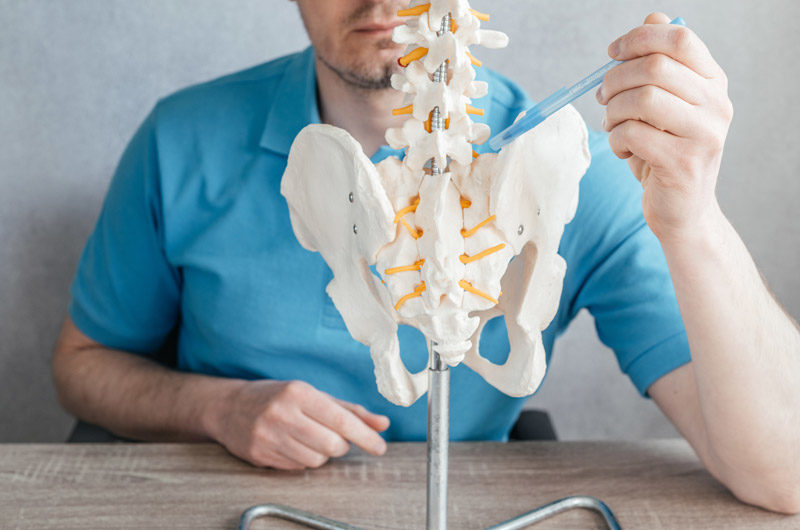
SIJ dysfunction
The sacroiliac (SI) joint is located next to the tailbone and the iliac portion of the pelvic bone. The joint acts as a shock absorber and does not move on its own. Symptoms of SIJ dysfunction include pain in the thigh or glutes that radiates down the back of the leg, usually on one side. Other symptoms include stiffness of the hips and lower back upon waking.
SIJ dysfunction may be caused by too much movement, not enough movement, pregnancy hormones, and the internal pressure of a growing baby. Treatment options include ice, heat, and rest, along with medication, supports or braces, chiropractic manipulations, physical therapy, sacroiliac joint injections, stem cell regeneration, and/or fusion surgery.
Spinal stenosis
Spinal stenosis occurs when the spaces within the spine narrow and put pressure on the nerves that travel through the spinal cord. The condition may occur in the lower back (lumbar stenosis) or neck (cervical stenosis). Symptoms include pain, tingling, numbness, and muscle weakness that may worsen over time. Some patients may not experience any symptoms.
The condition may be caused by bone overgrowth, herniated discs, thickened ligaments, tumors, and spinal injuries. To treat the condition, patients may need to take medications, receive steroid injections, and/or undergo physical therapy, decompression, or surgery. Surgery options include laminectomy, laminotomy, laminoplasty, and minimally invasive surgery.
section-201ef8f

section-004dbe9
Low back osteoarthritis
Low back osteoarthritis occurs when the layer of cartilage lining the facet joints in the spine breaks down and causes the bone to rub on bone. Symptoms of the condition include:
- Stiffness or tenderness in the low back
- Reduced range of motion and flexibility
- Dull, aching pain, or sharp pain during or after strenuous activity
- Muscle spasms in the low back
- Tingling, weakness, numbness or pain that radiates from the low back into the buttocks, thigh, or groin
Patients diagnosed with low back osteoarthritis may be treated with physical therapy, glucosamine supplementation, medication, and surgery.
Lumbar discopathy
Lumbar discopathy, also known as degenerative disc disease, can cause sharp pain in the lumbar and sacral curve, tingling, numbness, weakness, muscle tension, and pain originating from the nerve root in the sacral-lumbar curve.
The risk of lumbar discopathy may increase due to genetics, injuries, weight lifting, sitting for prolonged periods of time, working with vibrating equipment, age, narrow spinal channel, increased muscle tension, obesity, osteoporosis, and hormonal imbalances. Treatment options for lumbar discopathy include physical therapy, medications, weight loss, occupational therapy, and surgery.
